Carding Tutorial introduction
Carding become more sophisticated than ever, and what you can do about, read our Carding complete tutorial updated for beginners. After going through this Carding complete tutorial you will be able to get a view of of how carding ecosystem work and how this profitable carding industry is.
Usage of Credit cards as a mode of payment has being increasing rapidly and is one of the most widely used and convenient payment mode alternatives to cash. This mode of payment is now accessible to the common population of almost all the major geographical locations on our globe. Its ease of use and portability makes it a preferred mode of financial dealing. Such efficiency cannot be achieved without the presence of a large networked ecosystem connected through nodes of various computational devices. But, where there are computers and networks, there are hackers and carders.
carding Frauds related with Payment cards like Credit and Debit cards have raised serious privacy and authenticity concerns among its users. The recent few years have been worse hit where-in several major retail chains, ecommerce sites and brands were found to be affected with such frauds. The high monetary profit involved in this theft has attracted the biggest online cybercriminals and hackers to build their own empire with tightly knitted gang of individuals and groups. Most of the major payment card frauds are financially motivated and spans over several months starting from stealing the user information to conducting actual frauds. This carding tutorial goes into the details of how this entire carding ecosystem functions and how it is disrupting the current electronic payment industry at a large scale.
Carding in is not easy, you really need to devote your time to get success and money, So If you read our latest carding articles and tutorials, I guarantee you that within a week of real practising, you should be a pro carder.
Carding Key Vocabulary Terms
To start with, let us first give a quick read at some key vocabularies that will be used throughout this carding tutorial and will be relevant in further understating the key discussion points.
What is Carding?Carding is the process of obtaining unauthorized access to a card’s information and fraudulently using it for personal gain. Carding is not easy i confess, you'll need right information cc and bin for success. however you don't have to worry since everything is provided here.
Who is a CarderA carder is referred to as a person who makes use of Hacked credit card details or buys credit cards from Credit card shops, or even pick up Credit Cards from Dumps Via DarkWeb for the purpose of carding online shops.
What is Credit/Debit card(cc)?Lets Start our First topic "What is CC/DebitCard & Bins and types of Cards ? Types of Credit Card & Debit Card or Their starting digit;
Every Credit card company starts their credit card number with a unique number
to identify individually like shown below
A personal numeric value used to validate the card owner.
What is CVV/CVV2?3 or 4 digit number printed on the card. This number is used as an additional verification point to validate the cardholder.
What is BIN (Bank Identification Number)?The first six numbers of the card that is used to identify the issuing bank and in certain cases, the type of card.
What is BIN (Bank Identification Number)?Refers to the authorized companies whose network is used to facilitate the interaction between acquirer and issuer. Popular brands include Visa, Mastercard and American Express (Amex). A card starting with a 4 is a Visa, with a 5 is a Mastercard and with a 3 (15 digits long) is an Amex. A comprehensive list is provided later in the paper.
What is Buyer/Consumer:?The cardholder who purchases the goods and uses card for payments.
What is a Merchant:?Goods and service provider who accepts cards as a mode of payment.
What is a Acquirer Bank:?The bank responsible for processing the merchant’s credit card transactions with the buyer.
What is a Acquirer Bank:?The bank that issues credit card to the consumer.
What is an Issuer Bank:?The bank that issues credit card to the consumer
What is POS (Point Of Sale):?POS machines are the card reading devices used to carry out the monetary transaction between the buyer and merchant.
POS (Point Of Sale):?POS machines are the card reading devices used to carry out the monetary transaction between the buyer and merchant.
What is Magnetic Strip:?The black strip on the backside of the credit/debit card that stores various details required during financial transaction.
What is an Tracks:?Information on the magnetic strip is saved on tracks 1,2 and 3. The first two tracks are generally used to store the details like account number, owner name etc. The 3rd track is optional and used for storing additional data
What is Card dumps:?The raw un-encrypted data extracted from the temporary storage(RAM) of POS devices. These dumps carry information written on tracks 1 and 2 that are read by the POS device while making transactions.
What is a Runner:?The individual/group who uses the counterfeit cards to cash out from ATMs.
What is Card reader/Writer:?Is a piece of hardware and software that is used to write data onto the magnetic strip of the plastic card. MSR-206 is the most popular encoder used for writing data over cards.
What is Card Dropper:?The drop point for goods purchased online. The Dropper is usually an individual whose sole purpose is to receive the ordered item and deliver to the carder in return for cash or other goods.
What is Shopper:?Is the individual/group that does in-store shopping with counterfeit cards. These shoppers also carry fake IDs to make the fraud look more legitimate. Usually the carder can himself be a shopper or a runner.
What is EMV:?EMV or Chip-and-Pin cards are an alternative solution to swipe cards, which stores data on a chip in an encrypted manner. Even though the storage mechanism is encrypted, POS based malwares can still steal the data once it is decrypted in the memory.
What is Contactless RFID cards:?Another enhancement to traditional magnetic strip based cards. In RFID enabled cards, the buyer can pay for the goods by simply waving the card close to the POS terminal.
How cards payments are processed (Card present or card not Present)

Credit card transaction involves several steps before the payment is finalized. Here are the main steps involved during a transaction using credit card:
There is two types of credit card transactions:
- Card not present transaction
A card-not-present (CNP) transaction occurs when neither the cardholder nor the credit card is physically present at the time of the transaction. It's most common for orders that happen remotely — over the phone or by fax, internet, or mail
- Card present transaction
A card present transaction is one in which the customer physically interacts with payment machinery using his or her card.
How transactions are authorized?
Authorization hold (also card authorization, preauthorization, or preauth) is a service offered by credit and debit card providers whereby the provider puts a hold of the amount approved by the cardholder, reducing the balance of available funds until the merchant clears the transaction (also called settlement)
- Authorization: Cardholders request to purchase goods from using his credit card. The merchant submits transaction requests to acquirers. Acquirer then sends the transaction requests via cardholders’ card brand network to issuers. Issuer returns authorization codes via card brands’ networks to acquirers. Acquirers then forward authorization codes to merchant. If the transactions are authorized, merchants give cardholders the goods or service as requested
- Batching:
Merchants store an entire day’s authorized sales in a batch. At the end of the day, they send the batch via payment service providers to acquirers in order to receive payment.
- Clearing:
Acquirers send the batch via card brands’ networks to issuers in order to request payment. Card brands’ networks sort out each transaction to the right cardholders. Issuers then transfer requested funds via card brands’ networks to acquirers
- Funding:
Acquirer sends the payment to the merchant via the payment service provider. The payment is then billed and the amount is paid to the merchant.
These steps are just an outline of how the payments are processed using credit cards. There are several other authorization steps involved as well, but these four points form the major building block of the transaction phases.
Tools required to do carding
- Computer/Laptop or your Android
- Socks5 / VPN (Compulsory)
- Mac Address Changer (Not Compulsory)
- CCleaner
- Cc (Credit Card) Where to buy valid cvv Refundable
- M.A.C. Address Changer
- RDP
- CCleaner
- Mobile Phone or P.C.
- DROP
VPN or Socks
Do not be confused between Socks and VPN. Both are good, but if you can’t afford a premium VPN, opt for SOCKS5. Anytime you’re about to begin carding, endeavor to connect your Socks or VPN. Apart from hiding the I.P. address, you Mar not be able to card successfully, especially if you don’t stay in the U.S.
M.A.C. Address Changer
The M.A.C. address changer is a compulsory carding requirement. You just can’t do without the M.A.C. address changer as a carder who wants to be successful. As you read on, you will find out when to use this software while carding.
So the MAC stands for Media Access Control. This is like the uniqueness of every Network Interface Card (NIC).
A MAC address changer would allow you to change the MAC address of NIC ASAP. It is necessary to be safe and anonymous. Don’t forget this if you don’t want to get caught by the police.
RDP
The RDP is an acronym for the Remote Desktop Protocol. For this our carding tutorial, it will be very useful. It is an essential requirement for connecting to the computer of the geolocation of the victim with the CC you are targeting. It is as necessary as a VPN or SOCKS5; don’t fail to download one.
CCleaner
The CCleaner is useful for cleaning cache files and cookies from the browser. It also clears your browsing history and gives you an edge over the carding processes. Temporary browser files create a means for servers to track your activities. It Mar be easy to clear browser cookies, but tools like CCleaner can only remove flash cookies stored without your permission.
Mobile Phone or P.C.
If you’re using a mobile phone, disconnect from every Google service. The mobile phone must have at least 2GB ram and a sound processor. Before anything, root the phone to gain better control over your security.
If you can’t afford to root your current mobile phone, purchase a cheap Android phone of about $30 before you proceed. So if you are using a P.C. – M.A.C. or Windows, disable your location access. If possible, disable every location services in your P.C.
DROP
Drop simply means the shipping address which is used by the carder during carding. In this carding tutorial, you will see why it is important to have a DROP. Let me explain to you;
If you are carding with a US credit card and my shipping location is in Nigeria, the order won’t be shipped successfully. But if you use a US address as your shipping address – Marbe a picker, friend, or relative, then that is fine.
But if you don’t have anybody, there are companies that are called “DROP”. They are in the US, and that way they can help you ship your goods to their location – but you will pay an extra amount for that to happen. Now, the picker is the person that will pick up the carded item and forward to your location.
Types Of Carding
According to Pro carders, there are three types/levels of carding. They are listed as:
BIN
BIN is especially useful when you don’t have a complete CC. It is an acronym for Bank Identification Number and the first four digits of the CC number. In most cases, it is usually the first six digits. For example, if the card number is 6456 5466 6454 7456, the first 4-digit code being 6456 is BIN.
You can use the BIN to generate a virtual card for carding. It is an advanced level of carding you would learn with time.
CC Details
The CC is the essential requirement for carding to be successful. As a beginner in carding, you must devote time to understand how CC works and its components. Luckily for you, I will disclose everything you have to know about the CC right now.
CC refers to Credit Card, but in carding, we call it CC details. It is because when you pay for CC, you won’t receive a physical credit card. Instead, you’ll receive the details of the credit card in the form of Virtual Notepad.
The three kinds of CC You Can Buy
- Conventional CC
- Partial Full CC
- Full CC (CC Fullz)

The service CC is the regular CC you mostly find online, and it is less expensive. However, you can’t use it for so many carding processes due to limited details. I can only work on weaker websites.
Details in Regular CC
- Name:
- State:
- Address:
- City:
- Postal Code:
- Telephone Billing Number:
- Card Number:
- EXP.:
- CVV:
You can card sites like PayPal with these extra details.
The partially full CC includes more CC details, including:
- D.O.B.:
- SSN:
- Mother’s Maiden Name:
This CC is quite expensive, but it provides all the details to card any platform. If you can get this as a beginner and the knowledge of this carding tutorial, you stand a high chance of earning beyond $50 weekly.
The extra details in full CC include:
- Bank Name:
- Account Number:
- Routing Number:
- Bank Number:
- Drivers License Number:
- CC PIN
- Statuses of CC
It is advisable to confirm the CC balance so that you do not waste time on anything.
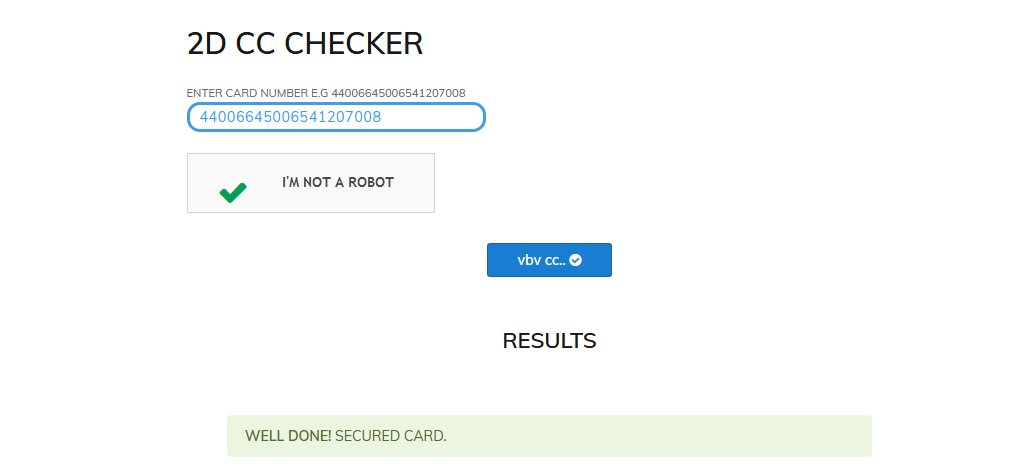
How to check CC validility
How to check non vbv bins cards - New non Checker Tool
To check if a credit or debit card is non vbv / 3D secure with out 2D checker tool.......
Read More..- Easy Carding:
At this level, a carder does carding of very cheap goods. For example, small phone call bills, etc. Mostly at this level, the carder uses to do carding of products below 50$. This is known as the beginner’s level of carding. - Intermediate Carding:
At this level, the carder does carding of slightly higher goods like background reports or very small physical items like some clothes. Mostly in this level, carders use to do carding of products below 50$. The difference between Level 1 and Level 2 carding is that Level 2 does the carding of physical items. - Hard Carding:
This is regarded as the advance carding. At this level, the carder does carding of everything. This includes cellphones, laptops, and other goods. Mostly in this level, the carder uses to do carding of products above 50$, and the upper limits are not fixed.
Entries point used by hacker to hack credit cards
Now that we have a fair amount of understanding about the credit cards system and how things are related, we can now move towards more technical details like the tutorial, the steps involved in carding method fraud transactions, identifying weak points etc. But before that, let us give a quick look at some common entry points used by the hackers in order to exfiltrate critical payment data.
Any credit card related theft involves following three steps:
- Reconnaissance
- Attack
- Sell
The financially motivated actor first studies the attack environment and tries to identify the weak points (Recon) that can be leveraged to craft an attack vector.
Once the weak points are identified, the attack phase begins. The main attack techniques include:
- Key logging
- Phishing
- Vulnerability Exploitation
- POS memory scrapping malware
Out of all these techniques, POS memory scrapping is the most widely implemented attack vector. The reason being it directly affects the device/medium that is used as a primary processing device for card based payment systems.
The point to note here is that, there has to be a delivery medium by which the POS malware gets introduced into the system. Phishing and vulnerability exploitation are the two popular ways of setting up a delivery mechanism for POS malware's. Insider threat has also been a key factor in infecting POS terminals. We will discuss POS malware's in brief here, as it is currently the talking point of this fraud ecosystem. It is the main weapon that is empowering the cybercriminals in targeting one of the biggest retail chains and brands across different regions

How credit cards and user logs data are hacked
During cyberattacks When you hear about a big hack in which millions of credit card numbers here is what usually happens. Hackers use various number of tools to steal data.
Below is three mainly used method used by cyber criminals to attain sensitive data.
- Skimming
Credit card skimming is a type of theft where the thief makes use of a device, known as a skimmer and steals the information of a credit card. When your credit card is swiped through the device, the skimmer will steal and store every detail that is on the magnetic stripe of the card
- Point of sales malware
Point of Sale or POS terminals are the main processing devices between the buyer and seller when a card based payment system is involved. POS based malware's are special purpose malware/virus program that are designed to scrape data from the terminal’s main memory. The idea is to steal the unencrypted data that gets copied to the terminal’s primary memory (RAM) when a credit or debit card is supplied to it for payment processing.
There is a slight misconception about POS devices that the data is sent to and fro in an encrypted manner. This is certainly true, but there is a short period of time when the POS terminal reads the data from cards and is stored in plain text manner in its primary memory before it gets encrypted again. This is where POS malware's comes into action and scrape the information from the memory.

A detailed discussion about the technical aspects of POS malware's is beyond the scope of this paper. Here I will summarize some key features/steps of this malware family that makes it a lethal weapon against plastic card based frauds:
- POS malware's include all the basic functionalities of a malware like data exfiltrating using networks, collecting system information, communicating with its command and control servers, kill switch to remove themselves from the infected system etc
- They have a specific purpose of scraping terminal’s memory and reading card data.
- They achieve this by first reading all the processes loaded into the device memory. They keep matching the running process names against their own local database to figure out which processes to scrape and which process to exclude.
- Once the processes are figured out, they can either execute custom functions or specific regular expressions in order to read data from the memory that matches with credit card information (Track 1 and 2 information).
- Once the data is scraped from memory, it is written onto the disk and stored at a specific location. Once the malware finds a live network connection on the terminal, and its parent controller is reachable(C&C server), it transfers that written file to its server (can be encrypted or un-encrypted) thus successfully exfiltrating the data.
Understanding the dump Track 1&2 data
Now that we have built up a background on how the POS terminals are infected and how the data is stolen, we can now have a brief overview of the data that POS malwares steal, how it looks like and how it is intercepted.
Here is an example of cleaned up data sent by a POS malware to its C&C server:
Track 1: B4096654104697113^ABHINAV/SINGH^08061012735900521000000
Track 2: 361344212572004=0512052335136; ABHINAV/SINGH
Track2 + Track1: 4411037117155348=14111010000013500000;
B4411037117155348^ABHINAV/SINGH^14111010000000135000000?
165430 | 134884 | 2 | 4921817934747226 | 4 | 2008 | 3 | 2010 | | 662 | ABHINAV
SINGH | 10 | VARUNA APP | VARANASI | PO139UX
468442/ 165337 | 134815 | 2 | 4921817809597243 | 3 | 2008 | 2 | 2010 | | 185
| ABHINAV SINGH | 10 | VARUNA | VARANASI | PR4 3HB | | lancs 01436672207
This looks like some random series of data dumped by the malware, but it is not. In order to make sense of this data, let us first spend few minutes on the structure of magnetic strip and the format in which it stores data on various tracks.
Dump Track 1 and 2 Block Diagram

Tracks are placed in a sequential order where Track 1 is followed by Track 2 and 3. The reading of data also follows the same order.
Track 1 and 2 are mostly used for storing crucial data. Track 3 is used for storing optional data. Depending on the banks choice, they can either store financial details either on Track 1 or Track 2. Both these tracks follow specific format for storing the data. Let us give a quick look at the block diagram of both these tracks to understand the format in which the data is stored and read on these tracks:
Both Track 1 and 2 store information in blocks where each block represents specific value, each having a particular storage limit and separated by delimiters.
Let us take the example of track 1 data dump once again and analyze it based on the fields we learnt in the block diagram:
Track 1: B4096654104697113^ABHINAV/SINGH ^08061012735900521000000?
Consider no values for SS and FC, The first seventeen characters represent the Bank Account number (B4096654104697113) followed by the field separator (^) and Account holder’s name (ABHINAV/SINGH). The next four characters represent expiry duration of the card in YYMM format (0806). The next few digits follows are the Service code (1012735900) and Identification number (521). The next few digits are the filers for the remaining bytes. Similarly we can also read the Track 2 data.
The point to note here is that Track 1 data is sufficient information when dealing with card dumps. It contains enough information to be converted into Track 2 dump as well. There are online tools available as well to do the conversion with ease. Trackgenerator.net is one such online service. Most of the online carding forums sell track 2 data.
- Phishing
Of course, chances are you wouldn't just open a random attachment or click on a link in any email that comes your way—there has to be a compelling reason for you to take action. Attackers know this, too. When an attacker wants you to install malware or divulge sensitive information, they often turn to phishing tactics, or pretending to be someone or something else to get you to take an action you normally would’t. Since they rely on human curiosity and impulses, phishing attacks can be difficult to stop.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
In an SQL injection attack, an attacker goes after a vulnerable website to target its stored data, such as user credentials or sensitive financial data. But if the attacker would rather directly target a website's users, they Mar opt for a cross-site scripting attack. Similar to an SQL injection attack, this attack also involves injecting malicious code into a website, but in this case the website itself is not being attacked. Instead, the malicious code the attacker has injected only runs in the user's browser when they visit the attacked website, and it goes after the visitor directly, not the website. User at the end are redirected on malicious websites.

Understanding carding ecosystem
Now because we have gathered knowledge about carding let us look at carding underground ecosystem.
There are three major steps involved in building a complete cybercrime ecosystem for credit card frauds. These are:
- Attack
- Sell
- Shop
Now we will move to the second step, which is to set up a shopping mall for the stolen data
Carding Forums
Carding forums (popular name) or dedicated websites for selling credit and debit card data are the most popular means of connecting with the mass newbie and elite group of people who have adopted this fraud as their full time profession. These forums are pretty similar in design and format, but what sets them apart is their source of dumps.
For Eg, a popular underground forum rescator.su, came into limelight when it was linked with selling dumps stolen from Target retail store breach (source: krebsonsecurity.com). Overnight, this store was flooded with tones of data. In my sequence of following this forum for couple of months, I noticed some key changes in their selling model, which was a result of customer complains and process improvement. The forum was re-designed to include couple of selection options for its buyers:
- Initially the dumps were only classified based on their brands like Visa, Mastercard, Amex etc.
- Initially the dumps were only classified based on their brands like Visa, Mastercard, Amex etc.
- • Later on, the city to which the details belong also became critical. So it was added as a filter criterion
- Banks and Payment networks continuously monitor payment transactions to detect fraud. Hence, oversea usage or out of city usage of card without notifying the banks was one trigger point. This is where buying dumps belonging to a particular country and city plays an important role.
- Later on an interesting feature was added which rates the success rate of a given card detail. This rating is based on factors like how old is the dump, how close it is to its expiry date, cards stature (platinum, titanium etc.). The CC details with lower success rate were relatively cheaper compared to those with higher success rate
Many forums and shop have increasing slowly. Last couple of years has seen an exponential rise in both sellers and buyers of carding frauds.
Buyers
Once the stolen card details are up for sale, the paddle starts rolling. The next entity that comes into picture is the buyers of these stolen details. Here are some key highlights from the role a buyer plays in this ecosystem:
The buyer profiles of these forums include newbies as well as experienced and regular customers. Both Buyer and seller gain more and more reputation based on their loyalty and frequent engagement.
The price of cards and dumps completely depend on the freshness and genre. On an average, a single Mastercard or Visa platinum card will range between $15 to $50. Buying dumps is relatively cheaper as it is a bulk purchase. Dumps price varies between $50 to $200 and contains on an average 10 card details. A bulk purchase of multiple dumps would cost between $600 to $5000 depending on the quantity and quality.
The download link to the dumps or card details is usually provided over a TOR based onion routing network to make sure that the location cannot be tracked back. IRC channels are also used actively for this purpose.https://t.me/JamesICQ742096688
Type of carding to cashout cc details
This is how the buyer gets introduced into this ecosystem and from here on, the buyer is the main driving element of the entire fraud ecosystem. Now the big question comes up is what would buyer do with the raw dumps supplied by the seller. The buyer now has two distinct options:
- Online Carding
- Offline/In-store Carding
Let us know more about each in detail.
Online Carding
Online carding is the process of using the stolen credit card details for purchasing goods online. This step involves some pre-steps before the buyer can go online and use the purchased card details for shopping. The first and the foremost important thing is knowing the CVV number. Most carding forums usually sell CVV details as well along with the card details. In case the CVV is not present, the buyer will have to follow some additional steps in order to obtain CVV number from the original owner of the card. These steps might include Phone phishing; fake postal mails asking for card verification etc. Buying “Fullz” is the most preferred option for online carding as It has all the required details.
Cardable websites
Once the CVV is available to the buyer, he now needs to figure out cardable websites. Cardable websites are those website that meet the following criteria:
- Making sure that the website’s terms and conditions do not specifically ship items only to the card’s registered address. It should ship to other shipping address mentioned during purchase as well.
- Making sure that International shipping is allowed.
- The next thing to look for is weather the website has Visa verification code or Mastercard secure code enabled. This is a two-step authentication where the payment gateway asks for a secure code before proceeding with payment. The card owner only knows this secure code
- . Check for additional security measures like card scans, delivery at door even when there is no one home, call backs to confirm item payment etc.
It is not easy to find such websites but professional fraudsters are good at finding work around. Several Gambling and online casino websites usually don’t have such strong security measures thus giving a good scope for fraudsters to add money to their gambling account. Buying porn website subscriptions, buying crypto currency, online betting and gaming are few other popular ways of using CC for online carding. Underground forums are a good place for finding new and updated list of cardable websites. The community is tightly knitted and carders keep posting their findings into these forums to make sure that the ecosystem is ticking. nonvbvshop@outlook.com
- American Express (AMEX Card) – 3
- Visa Card – 4
- Master Card – 5
- Discover (Disco) – 6
- VBV Cards
- NonVbv cc Cards
- Mscs Card
- Non Mscs card
For Doing Successful Carding U need a Perfect bin for each website So, Lets learn about what is Bin and how to check bin of any CC/Debit
What is BIN?
It is known as Bank Identification Number (BIN). It is a 6-digit number e.g.: 431408. Some of the reference sites which give BIN info which I also refer:
- www.bins.pro
- www.bindb.com
- www.binlists.com
- www.exactbins.com
Simply go to the site (www.bins.pro) enter BIN(Enter First 6 digit of card number) and click on find to get the details.
What is the meaning of VBV , NON VBV and MSC,Non MsC ?VBV (Verified by Visa) – Extra level protection is added by Visa to protect the Card from fraud. Like DOB, password, Social Security Number and Mother’s name, etc. also sending OTP (one-time password) as extra security level to card owner mobile number to validate the transaction.
NON - VBV NON VBV (Verified by Visa) –Handy to use. No need extra information as specified in VBV card while doing the transaction.Note it down (IMP)- Carders mainly buy and use NON VBV cards for carding. MSC (MasterCard Secure Code) – security level same as VBV card. Non MsC-same security level as Non Vbv have
DROP
DROP is an address which the carder uses for the shipping address in the carding process. Let me explain in details with an example: If I am carding with US credit card, then I use USA address as shipping address then
my order will be shipped successfully, and I will be safe. If you have relatives/friends, then no problem, otherwise use sites who provide drop services only we have to pay extra for shipping it.
Why we need Drop coz if we are carding with UsA cc and putting shipping address of other country in that case there is 90% chance that our order got cancelled.
Now Lets Learn About Category of Visa & MasterCard
Category Of Visa CC- Classic: The Card is used worldwide in any locations designated by Visa, including ATMs, real and virtual Stores, and shops offering goods and services by mail and telephone.
- Gold – This card has a higher limit capacity. Most used card and adopted worldwide.
- Platinum – Card is having limits over $10,000.
- Signature – No preset spending limit – great bin to get
- Infinite – Most prestigious card with having virtually no limit. There is less in circulation so be alert when buying these. Use only with reputable sellers!
- Business – it can be used for small to medium sized businesses, usually has a limit
- Corporate – it can be used with medium to large size businesses, having more limit than a Business card
- Black – It has limited membership. It has no limit only having $500 annual fee, high-end card.
- Classic: it is same as classic visa card.
- Gold – it is same as Gold visa card.
- Platinum – it is same as visa platinum card
- World – it has a very high limit
- World Elite – it is virtually no limit, high-end card.
- Gold – it usually has around a 10k limit.
- Platinum- is usually has a higher limit (around 35k).
- Centurion – it has a High limit (75k+). It is also known as the black card, note: do not confuse with visa black card.
Carding easy step by step tutorial
To proceed with the next step make sure you have the following carding tools ready.
Credit Card, Socks5 also known as SOCKS5 Proxy which mask your identity, making your location matching with the CC owner address,
CCleaner Software, High-Speed internet and lastly your VPN(so all your activities gets encrypted and safe).
- Create a new Email account with the matching name of CC holder. If CC holder’s name is Smith Parker then make something like Smithparker78@***.com Note: Never use disposable Emails for carding.
- Run RDP and connect with your Host, in case you are not using RDP , follow the steps below
- Change all the MAC addresses using MAC Address Changer.
- Clear all the history of your PC including Cache, Temp Files using CC Cleaner.
- Set up sock5 in Mozilla Firefox, check above I have explained how to setup socks in Mozilla.
- Now, restart your browser and visit This link to check if your IP has changed with the location of CC holder or not
- Open any local online market store, I will suggest you use anyone which is from your own country.
- Register a new account with the name of CC holder and Email you made for carding.
- Try to add an item to your cart, the item should below USD $500, never use big orders for the first transaction.
- In shipping address, add the address where you want to deliver the product.
- Now, go for the payment option, choose credit card for payment.
- Enter all the credit card details you received when you bought the credit card.
- For the Billing address, use the address of CC Holder.
Conclusions
To quickly summarize our learning so far: we have seen how the plastic payment networks work. Then we read about the different threats that posses to these electronic payments. We then emphasized on POS malware's and their behavior. Then we saw what kind of information this malware steal. Now we will move to our actual agenda: How this stolen information forms the crux of an ever profitable cyber crime
Thank all for reading our carding tutorial.